Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kamwang, N.*; Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 4th Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-4) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/07
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko; Suzuki, Takashi
Proceedings of 4th Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-4) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/07
The Facility of Radiation Standards (FRS) in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides beta-ray calibration fields for the customers to calibrate dosemeters. Two different types of beta-ray irradiation systems, so called BSS2 and JBS, have been installed and operated in the FRS. They have quite different types of the beta-ray radiation sources, which might be attributed to variations in dosimetric quantities. Variations in these quantities would affect the calibration factor of a dosemeter. A comparison of dosimetric quantities for beta reference radiation fields of both beta-ray irradiation systems was made, in order to investigate how these quantities differ between them and how much differences affect calibration results. With regard to the depth dose curve which is one of the key dosimetric quantities, it was found that they showed different profiles between both systems reflecting their characteristics. This implies that the difference between two systems might affect the calibration of dosemeters, especially one with more than 400 mg/cm thickness or one made of high-Z materials for
thickness or one made of high-Z materials for  Sr/
Sr/ Y field.
Y field.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko*; Tatebe, Yosuke; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Kawasaki, Katsuya; Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshizawa, Michio; Shimizu, Shigeru*; Kim, J.-S.*; Lee, J.-G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 4th Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-4) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/07
 Np and
Np and  Am in near-surface environments
Am in near-surface environmentsTanaka, Tadao; Ya-Anant, N.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.303 - 306, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Laboratory scale experiments were performed to investigate migration behavior of  Np and
Np and  Am, which were deposited onto the ground surface from spent fuel reprocessing facilities, in near-surface environment. Column migration experiments were conducted by varying the volume of eluting solution, for a sandy soil and a reddish soil. There seemed to be two chemical species of
Am, which were deposited onto the ground surface from spent fuel reprocessing facilities, in near-surface environment. Column migration experiments were conducted by varying the volume of eluting solution, for a sandy soil and a reddish soil. There seemed to be two chemical species of  Np in the sandy soil column; one is cationic and the other is particulate form. The particulates moved without significant interaction with the sandy soil. The sorption of cationic
Np in the sandy soil column; one is cationic and the other is particulate form. The particulates moved without significant interaction with the sandy soil. The sorption of cationic  Np was controlled by both a reversible ion-exchange reaction and irreversible reactions. Most of
Np was controlled by both a reversible ion-exchange reaction and irreversible reactions. Most of  Am formed rather large particulates and trapped in the sandy soil column. The
Am formed rather large particulates and trapped in the sandy soil column. The  Np and
Np and  Am loaded into the reddish soil column moved deeper with increasing eluting volume. The sorption was mainly controlled by ion-exchange reaction. The migration behavior could be significantly evaluated by the distribution coefficient.
Am loaded into the reddish soil column moved deeper with increasing eluting volume. The sorption was mainly controlled by ion-exchange reaction. The migration behavior could be significantly evaluated by the distribution coefficient.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sato, Kaoru; Endo, Akira; Ono, Koji*; Yoshitake, Takayasu*; Hasegawa, Takayuki*; Katsunuma, Yasushi*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Kai, Michiaki*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.241 - 243, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:81.61(Environmental Sciences)A web-system of WAZA-ARI is being developed to assess radiation dose to a patient in a Computed Tomography (CT) examination. WAZA-ARI utilizes a set of organ and tissue doses in a database for the dose assessment, according to the given resources with a consideration of the examination condition. The organ and tissue doses in the database have been derived with the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS. Modeling of the patient was a significant issue in the radiation transport calculation. JM phantom, whose height (171 cm) and weight (65 kg) are near to those averaged over Japanese male adults, was incorporated to PHITS as a human model. Since JM phantom consisted of about 1 mm size voxel, the shapes could be realistically reproduced even for small organs such as thyroid, adrenals. Masses of most organs could be also adjusted to the averaged values of Japanese male adults. In addition, our calculations introduced a new phantom without arms based upon JM phantom, because the patient usually puts arms toward the head direction in a torso examination. Some of organ doses calculated by JM phantom were compared with results, which were derived with a MIRD-type phantom. Differences could be seen in some organ doses between the phantoms, if photon attenuations in a shaping (Bow-tie) filter were taken into account to a source model in PHITS.
size voxel, the shapes could be realistically reproduced even for small organs such as thyroid, adrenals. Masses of most organs could be also adjusted to the averaged values of Japanese male adults. In addition, our calculations introduced a new phantom without arms based upon JM phantom, because the patient usually puts arms toward the head direction in a torso examination. Some of organ doses calculated by JM phantom were compared with results, which were derived with a MIRD-type phantom. Differences could be seen in some organ doses between the phantoms, if photon attenuations in a shaping (Bow-tie) filter were taken into account to a source model in PHITS.
Ban, Nobuhiko*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Ono, Koji*; Hasegawa, Takayuki*; Yoshitake, Takayasu*; Katsunuma, Yasushi*; Sato, Kaoru; Endo, Akira; Kai, Michiaki*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.244 - 247, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:81.61(Environmental Sciences)We are developing a web-based system, WAZA-ARI, for the dose calculation of patients undergoing X-ray CT examinations. Tissue doses were calculated in a Japanese adult male phantom (JM phantom) using a Monte Carlo code, PHITS, and the normalized dose coefficient data are stored as XML files. The system is implemented in Java on a Linux server running Apache Tomcat, which is accessed via a web browser over a network. Users are requested to choose scanning options and to input parameters in the data entry screen. The corresponding dose data are called upon input, and they are summed over the scan range specified by the user to estimate unit tissue doses. Tissue doses are computed based on the radiographic exposure (mAs), the beam pitch and air kerma at the beam center on the axis of rotation. Users can also use their own air kerma, CTDI vol and DLP values for the dose computation instead of the default setting. Although the dose coefficients are prepared for only limited CT scanner models currently, our system has achieved high usability and easy maintenance without commercial software. Possibility of further expansion for the practical application is also discussed.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Endo, Akira; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Niita, Koji*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.183 - 185, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.73(Environmental Sciences)A set of the conversion coefficients from fluence to the effective dose has been calculated for neutrons and protons over wide energy ranges based on the instruction given in ICRP 103, using the PHITS code. The calculated values are generally smaller than those based on ICRP Publication 60, predominantly owing to the revision of 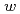
 for those particles. The impact of the introduction of ICRP 103 on the dosimetry for high-energy particles will be discussed by comparing between the ICRP 103- and ICRP 60-based effective doses for aircrews as well as workers in high-energy accelerator facilities.
for those particles. The impact of the introduction of ICRP 103 on the dosimetry for high-energy particles will be discussed by comparing between the ICRP 103- and ICRP 60-based effective doses for aircrews as well as workers in high-energy accelerator facilities.
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.140 - 143, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Radiation workers engaging in the fabrication of MOX fuels are exposed to neutrons, and hence thermoluminescent albedo dosemeters (TLAD) need to be used at JAEA-NCL. Because estimating the doses using TLADs are susceptible to the neutron energy spectrum, the authors have issued TLADs incorporating Solid-State Nuclear Tracks Detectors (SSNTDs) to selected workers who are routinely exposed to neutrons and been analyzing the relationship between the SSNTD and the TLAD (T/Rf) over the past 6 years. Consequently, the  /
/
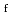 in each year was 10-20 (3.363 mm
in each year was 10-20 (3.363 mm )/(mSv
)/(mSv  Cs eq.), which is smaller than the data during 1991-1993, although the neutron spectra had not changed compared with that of the early 1990s. This decrease of the
Cs eq.), which is smaller than the data during 1991-1993, although the neutron spectra had not changed compared with that of the early 1990s. This decrease of the  /
/
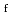 implies that the ratio of work carried out nearby the gloveboxes to total work decreased.
implies that the ratio of work carried out nearby the gloveboxes to total work decreased.
Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yonehara, Hidenori*; Kosako, Toshiso*; Fujitaka, Kazunobu*; Sasaki, Yasuhito*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.123 - 125, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.96(Environmental Sciences)The National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) has helped the airlines companies to follow the guideline, particularly for the calculation of aviation route doses. The presentation will show the annual individual doses of aircraft crew calculated for the 2007 fiscal year.
Nakamura, Keisuke; Maeda, Makoto*; Yasumune, Takashi*; Maehata, Keisuke*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; Tanaka, Keiichi*; Umeno, Takahiro*; Takasaki, Koji; Momose, Takumaro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.88 - 91, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.73(Environmental Sciences)A Transition Edge Sensor (TES) microcalorimeter has been developed for use as an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer. A TES microcalorimeter is a thermal detector used to measure the energy of an incident photon with increase in temperature. In this work, a TES microcalorimeter with a 5 m Au absorber was developed for use in measuring LX rays emitted from transuranium elements. Furthermore, as a cooling system a dilution refrigerator utilizing a Gifford-McMahon refrigerator was used, which needs no liquid helium. The performance of the TES microcalorimeter was evaluated by measuring the LX rays emitted by an
m Au absorber was developed for use in measuring LX rays emitted from transuranium elements. Furthermore, as a cooling system a dilution refrigerator utilizing a Gifford-McMahon refrigerator was used, which needs no liquid helium. The performance of the TES microcalorimeter was evaluated by measuring the LX rays emitted by an  Am source. This system proved effective in the measurement of the LX rays because the full width at half maximum of the L
Am source. This system proved effective in the measurement of the LX rays because the full width at half maximum of the L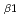 X ray was about 80 eV.
X ray was about 80 eV.
 -
- coincidence method for selective measurement of
coincidence method for selective measurement of  Bi-
Bi- Po; Application to dust filter used in radiation management
Po; Application to dust filter used in radiation managementSanada, Yukihisa; Tanabe, Yoichiro*; Iijima, Nobuo; Momose, Takumaro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.80 - 83, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.29(Environmental Sciences)The radionuclide pair  Bi and
Bi and  Bi which belongs to the uranium-series interferes with airborne radionuclide measurement, needed for the radiation management of a nuclear facility. Time intervals between
Bi which belongs to the uranium-series interferes with airborne radionuclide measurement, needed for the radiation management of a nuclear facility. Time intervals between  Bi (
Bi ( ) and
) and  Po (
Po ( ) are much shorter than artificial radionuclides due to the short half-life of
) are much shorter than artificial radionuclides due to the short half-life of  Po (164
Po (164  s). Measurement of airborne radionuclides can subtract this background by the selective measurement of
s). Measurement of airborne radionuclides can subtract this background by the selective measurement of  Bi-
Bi- Po. The purpose of this study is to develop of a new analytical method (Time interval analysis: TIA) based on the beta-alpha coincidence method for selective measurement of
Po. The purpose of this study is to develop of a new analytical method (Time interval analysis: TIA) based on the beta-alpha coincidence method for selective measurement of  Bi-
Bi- Po. The developed method was applied to an actual dust-filter measurement.
Po. The developed method was applied to an actual dust-filter measurement.
Hashimoto, Makoto; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Kosako, Toshiso*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.65 - 68, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)A dose evaluation using multiple radiation detector outputs can be improved by the convex optimisation. It enables flexible dose evaluation corresponding to the radiation field. The neutron ambient dose equivalent is evaluated using a mixed-gas proportional counter. The reliability of evaluated dose values are comparable with current dosimeter. An application to neutron individual dose equivalent measurement is also investigated. The combination of dosimeters with high orthogonality of response characteristics tends to show good suitability for dose evaluation.
Kinase, Sakae; Mohammadi, A.; Takahashi, Masa; Saito, Kimiaki; Zankl, M.*; Kramer, R.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.191 - 194, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.59(Environmental Sciences)Endo, Kuniaki; Momose, Takumaro; Furuta, Sadaaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.119 - 122, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.65(Environmental Sciences)Usui, Toshihide; Takashima, Hideki; Iwasa, Atsutoshi; Hamazaki, Masaaki
Proceedings of 3rd Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-3) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2010/05
Okura, Takehisa; Yamazawa, Hiromi*; Moriizumi, Jun*; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Guo, Q.*; Tojima, Yasunori*; Iida, Takao*
Proceedings of 3rd Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-3) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2010/05
Monitoring network of  Rn concentration in air which was measured in Beijing, Nagoya, Hegura-jima, Hachijo-jima and Hateruma-jima, as a tracer for long-range transport in East Asia was established. At inland sites, Beijing and Nagoya, high concentrations
Rn concentration in air which was measured in Beijing, Nagoya, Hegura-jima, Hachijo-jima and Hateruma-jima, as a tracer for long-range transport in East Asia was established. At inland sites, Beijing and Nagoya, high concentrations  Rn were measured, at marine sites, Hachijo-jima and Hateruma-jima,
Rn were measured, at marine sites, Hachijo-jima and Hateruma-jima,  Rn concentrations level was very low. Seasonal variations of the
Rn concentrations level was very low. Seasonal variations of the  Rn concentration show that
Rn concentration show that  Rn concentration was the lowest in the summer and the highest in the winter. Diurnal variations were measured at inland sites. At marine sites several-day-cycle variations were measured. It was pointed out by this study that the several-day-cycle variations at Hachijo-jima were dependent on synoptic-scale atmospheric disturbance. Backward trajectory analysis of the relationship between atmospheric
Rn concentration was the lowest in the summer and the highest in the winter. Diurnal variations were measured at inland sites. At marine sites several-day-cycle variations were measured. It was pointed out by this study that the several-day-cycle variations at Hachijo-jima were dependent on synoptic-scale atmospheric disturbance. Backward trajectory analysis of the relationship between atmospheric  Rn concentrations at Hachijo-jima and transport pathway of air mass indicates that atmospheric
Rn concentrations at Hachijo-jima and transport pathway of air mass indicates that atmospheric  Rn at Hachijo-jima has much to do with transport pathway of air.
Rn at Hachijo-jima has much to do with transport pathway of air.
Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Tsujimura, Norio; Yamano, Toshiya*
Proceedings of 3rd Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-3) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2010/05
A neutron survey meter with a ZnS(Ag) scintillator to measure recoil protons was built. The detection probe weighs approx. 2 kg, therefore providing us with true portability. Performance tests exhibited satisfactory neutron dosimetry characteristics at unmoderated or lightly moderated fission neutron fields and in particular work environments at a MOX fuel facility. This new survey meter will augment a routine neutron monitoring inconveniently being carried out by moderator-based neutron survey meters.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Takada, Chie
Proceedings of 3rd Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-3) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2010/05
To predict how accurately the neutron dosemeters can measure the neutron dose equivalent (rate) in MOX fuel fabrication facility work environments, the calculations of the dose equivalent responses of neutron dosemeters were performed by the spectral folding method. The dosemeters selected included two types of personal dosemeters (a thermoluminescent albedo neutron dosemeter and an electronic neutron dosemeter), three moderator-based neutron survey meters and one special instrument called an 
 (10) monitor. The calculations revealed the energy dependences of the responses expected within the entire range of neutron spectral variation observed in neutron fields at workplaces.
(10) monitor. The calculations revealed the energy dependences of the responses expected within the entire range of neutron spectral variation observed in neutron fields at workplaces.
Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakano, Masanao; Sumiya, Shuichi; Nemoto, Hiromi*; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*
Proceedings of 3rd Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-3) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/05
The dose to the public at hypothetical accident of nuclear facility is estimated on the basis of the method described in the Japanese meteorological guideline. However, the radioactive decay during atmospheric dispersion of released radionuclide is not considered in the calculation formula in the guideline. Therefore, when the radionuclide of the half life such as a few min is released, the dose may be excessively over-estimated. In this study, the calculation code was developed which could consider the radioactive decay of the released radionuclide and the generation of the product. The dose calculated on the basis of the developed code was compared with that on the basis of the guideline.
Kanai, Katsuta; Kurihara, Osamu
Proceedings of 3rd Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-3) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2010/05
Chest wall thickness (CWT) of the subject is an important modifier to determine the lung burden of inhaled actinides such as Pu isotopes or  Am through lung counting. CWT prediction equations as a function of biometric indexes have been proposed by many authors based on chest wall measurements made with an ultrasound device. In the present study we derived such equations from CWT data of our subjects and then evaluated their applicability to monitoring with our currently used lung counter, mainly examining the accuracy of determinations of
Am through lung counting. CWT prediction equations as a function of biometric indexes have been proposed by many authors based on chest wall measurements made with an ultrasound device. In the present study we derived such equations from CWT data of our subjects and then evaluated their applicability to monitoring with our currently used lung counter, mainly examining the accuracy of determinations of  Am, useful as a unique indicator that can be detected in most cases of internal contamination with Pu compounds. The error of the equations obtained was found to be within the range of - 8 mm to + 6 mm against actual CWT values of our subjects, complying with the bias performance criteria for direct measurements. However, further studies might be needed to clarify the effect of the difference in posture on the CWT caused by the modification of the counting geometry made for our lung counter.
Am, useful as a unique indicator that can be detected in most cases of internal contamination with Pu compounds. The error of the equations obtained was found to be within the range of - 8 mm to + 6 mm against actual CWT values of our subjects, complying with the bias performance criteria for direct measurements. However, further studies might be needed to clarify the effect of the difference in posture on the CWT caused by the modification of the counting geometry made for our lung counter.